Route Table Overview¶
A custom route is route that you add to a VPC route table.
A custom route is route that you add to a VPC route table.
Route Table¶
A route table contains a set of routes that are used to determine where network traffic from your subnets in a VPC is directed. Each subnet must be associated with a route table. A subnet can only be associated with one route table at a time, but you can associate multiple subnets with the same route table.
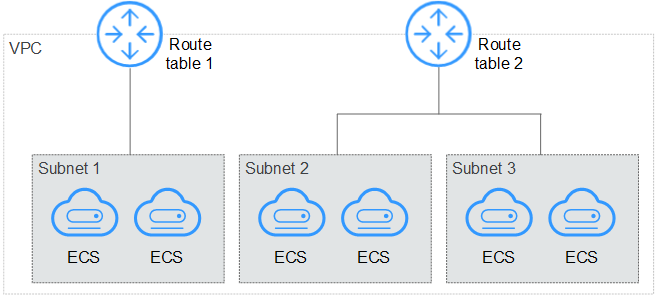
Figure 1 Route table¶
Default Route Table and Custom Route Table¶
When you create a VPC, the system automatically generates a default route table for the VPC. If you create a subnet in the VPC, the subnet automatically associates with the default route table. You can add, delete, and modify routes in the default route table, but you cannot delete the route table. When you create a VPN, Direct Connect connection, the default route table automatically delivers a route that cannot be deleted or modified. If you want to modify or delete the route, you can associate your subnet with a custom route table and replicate the route to the custom route table to modify or delete it.
If you do not want to use the default route table, you can now create a custom route table and associate it with the subnet. You can delete the custom route table if it is no longer required.
Note
The custom route table associated with a subnet affects only the outbound traffic. The default route table determines the inbound traffic.
For details about how to create a custom route table, see section Creating a Custom Route Table.
Route¶
A route is configured with the destination, next hop type, and next hop to determine where network traffic is directed. Routes are classified into system routes and custom routes.
System routes: These routes are automatically added by the system and cannot be modified or deleted.
After a route table is created, the system automatically adds the following system routes to the route table, so that instances in a VPC can communicate with each other.
Routes whose destination is 100.64.0.0/10 or 198.19.128.0/20.
Routes whose destination is a subnet CIDR block.
Note
In addition to the preceding system routes, the system automatically adds a route whose destination is 127.0.0.0/8. This is the local loopback address.
Custom routes: These are routes that you can add, modify, and delete. The destination of a custom route cannot overlap with that of a system route.
You can add a custom route and configure the destination, next hop type, and next hop in the route to determine where network traffic is directed. Table 1 lists the supported types of next hops.
Table 1 Next hop type¶ Next Hop Type
Description
Supported Route Table
Server
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to an ECS in the VPC.
Default route table
Custom route table
Extension NIC
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to the extension NIC of an ECS in the VPC.
Default route table
Custom route table
VPN connection
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to a VPN gateway.
Custom route table
Direct Connect gateway
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to a Direct Connect gateway.
Custom route table
VPC peering connection
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to a VPC peering connection.
Default route table
Custom route table
Virtual IP address
Traffic intended for the destination is forwarded to a virtual IP address and then sent to active and standby ECSs to which the virtual IP address is bound.
Default route table
Custom route table
Note
If you specify the destination when creating a resource, a system route is delivered. If you do not specify a destination when creating a resource, a custom route that can be modified or deleted is delivered.
When you create a VPN connection or a Direct Connect gateway, you need to specify the remote subnet, that is, the destination of a route. In this case, the system delivers this system route. Do not modify the route destination on the Route Tables page. If you do, the destination will be inconsistent with the configured remote subnet. To modify the route destination, go to the specific resource page and modify the remote subnet, then the route destination will be changed accordingly.
Custom Route Table Configuration Process¶
Figure 2 shows the process of creating and configuring a custom route table.
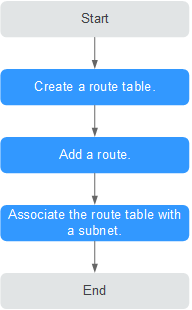
Figure 2 Route table configuration process¶
For details about how to create a custom route table, see Creating a Custom Route Table.
For details about how to add a custom route, see Adding a Custom Route.
For details about how to associate a subnet with a route table, see Associating a Subnet with a Route Table. After the association, the routes in the route table control the routing for the subnet.
Notes and Constraints¶
A maximum of 10 route tables, including the default one, can be created for each VPC.
A maximum of 200 routes can be added to each route table.
The default route table cannot be deleted.
The system route cannot be modified or deleted.
The routes delivered by the VPN service to the default route table cannot be modified, replicated, or deleted.
The routes delivered by the Direct Connect service to the default route table cannot be modified or deleted.
If the Direct Connect service is enabled in the self-service mode, the routes delivered to the default route table can be replicated to the custom route table.
If the Direct Connect service is enabled by call or email, the routes delivered to the default route table cannot be replicated to the custom route table.
Black hole routes cannot be replicated.
When you add a custom route to a default route table, the next hop type cannot be set to VPN connection or Direct Connect gateway.