How Do I Troubleshoot an Unhealthy Backend Server?¶
Symptom¶
If a client cannot access a backend server through a load balancer, the backend server is declared unhealthy. You can view the health check results for a backend server on the ELB console.
On the Load Balancers page, click the name of the load balancer to view its details. Click Backend Server Groups and locate the server group. You can find the health check results for backend servers in the Basic Information area.
Background¶
Load balancers use the IP addresses from the VPC where the load balancers work to send heartbeat requests to backend servers. To ensure that health checks can be performed normally, you need to ensure that the IP addresses from the VPC where the load balancers work are allowed to access the backend servers.
Caution
Ensure that security group rules allow access from IP addresses in the CIDR block of the VPC where the backend server resides.
For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules for Backend Servers.
If Cross-VPC Backend is not enabled for a load balancer and a TCP or UDP listener is added to the load balancer, there is no need to configure security group rules to allow traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to the backend servers associated with TCP or UDP listener.
If a backend server is considered unhealthy, ELB will not route traffic to it until it is declared healthy again.
Note
When a backend server is detected as unhealthy, the load balancer will stop routing requests to this server.
If health checks are disabled, the load balancer will consider the backend server healthy by default and still route requests to it.
Traffic will not be routed to a backend server with a weight of 0, so the health check result for this backend server is not relevant.
Troubleshooting¶
Possible causes are described here in order of their probability.
Check these causes one by one until the cause of the fault is determined.
Note
If you need to change the health check configuration, it takes a while for the changes to be applied. The required time depends on the health check interval and timeout duration. You can find the health check results in the backend server list of the load balancer.
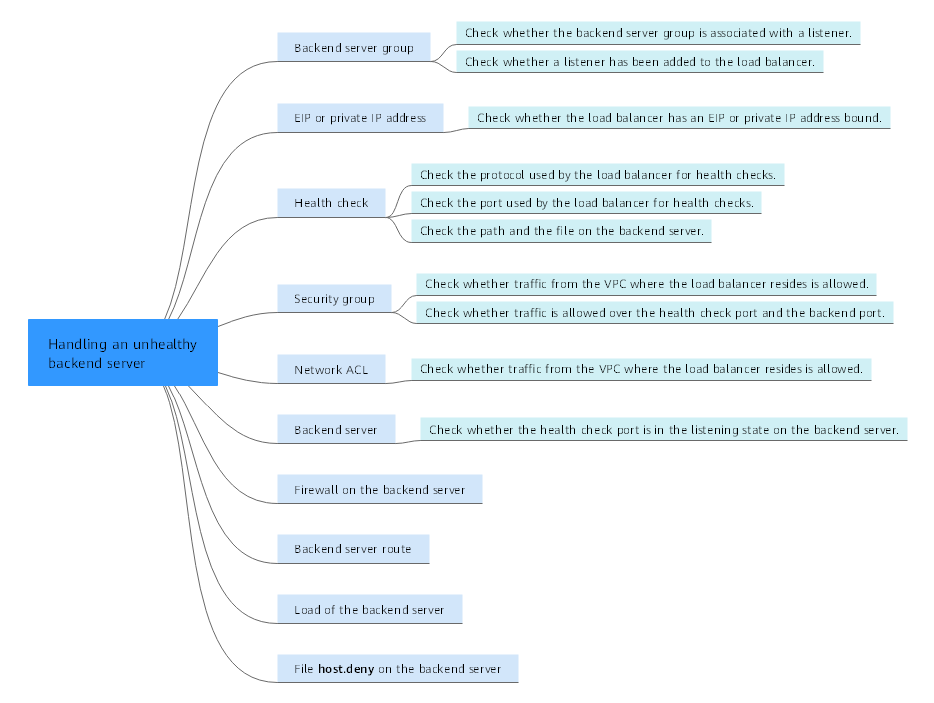
Figure 1 Troubleshooting process¶
Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
Backend server group | Checking Whether the Backend Server Group Is Associated with a Listener |
EIP or private IP address | Checking Whether an EIP or a Private IP Address Is Bound to the Load Balancer |
Health check configuration | |
Security group rules | |
Network ACL rules | |
Backend server listening configuration | |
Backend server firewall configuration | |
Backend server route configuration | |
Backend server load | |
Backend server host.deny file |
Checking Whether the Backend Server Group Is Associated with a Listener¶
Check whether the backend server group that the unhealthy backend server belongs to is associated with a listener.
If the backend server group is not associated with a listener, check whether a listener has been added to the load balancer.
If there is a listener, associate the backend server group with the listener.
If there are no listeners, add a listener. Select Use existing and then select the backend server group when you add the listener.
If the backend server group has been associated with a listener, proceed with the following operations.
Checking Whether an EIP or a Private IP Address Is Bound to the Load Balancer¶
Note
Check this only when you add a TCP or UDP listener to the load balancer.
If you add an HTTP or HTTPS listener to the load balancer, health checks will not be affected no matter whether an EIP or private IP address is bound to the load balancer.
If you add a TCP or UDP listener to the load balancer, check whether the load balancer has an EIP or private IP address bound.
If the load balancer has no EIP or private IP address bound, bind one.
Note
When you create a load balancer for the first time, if no EIP or private IP address is bound to the load balancer, the health check result of backend servers associated with a TCP or UDP listener is Unhealthy. After you bind an EIP or private IP address to the load balancer, the health check result becomes Healthy. If you unbind the EIP or private IP address from the load balancer, the health check result is still Healthy.
Checking the Health Check Configuration¶
Click the name of the load balancer to view its details. On the Backend Server Group tab page, click the name of the backend server group. In the Basic Information area, to the right of Health Check, click Configure and then check the following parameters:
Protocol: The protocol used for health checks.
Port The port must be the one used on the backend server, and it cannot be changed. Check whether the health check port is in the listening state on the backend server. If the health check port is not in the listening state on the backend server, the backend server will be identified as unhealthy.
Check Path If HTTP is used for health checks, you must check this parameter. A simple static HTML file is recommended.
Note
If the health check protocol is HTTP, the port and the path are used for health checks.
If the health check protocol is TCP, only the port is used for health checks.
If health check protocol is HTTP and the health check port is normal, change the path or change the health check protocol to TCP.
Enter an absolute path.
For example:
If the URL is http://www.example.com or http://192.168.63.187:9096, the health check path is /.
If the URL is http://www.example.com/chat/try/, the health check path is /chat/try/.
If the URL is http://192.168.63.187:9096/chat/index.html, the health check path is /chat/index.html.
Checking Security Group Rules¶
TCP, HTTP, or HTTPS listeners: Verify that the inbound security group rule allows TCP traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to the backend server over the health check port.
Caution
Load balancer: If Cross-VPC Backend is not enabled for a load balancer that has a TCP or UDP listener, there is no need to configure security group rules and firewall rules to allow traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to the backend servers associated with TCP or UDP listener.
If the health check port is the same as the backend port, the inbound rule must allow traffic over the backend port, for example, port 80.
If the health check port is different from the backend port, the inbound rule must allow traffic over both the health check port and backend port, for example, ports 443 and 80.
Note
You can check the protocol and port in the Basic Information area of the backend server group.
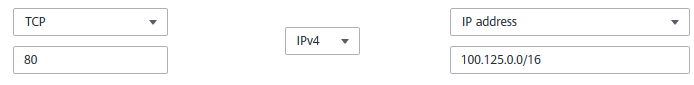
Figure 2 Example inbound rule¶
UDP listeners: Verify that the inbound security group rule allows traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to the backend server using the health check protocol and over the health check port. In addition, inbound ICMP traffic must be allowed.
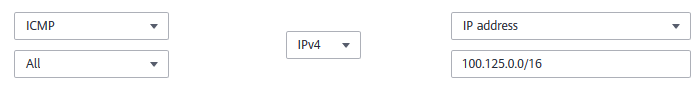
Figure 3 Example inbound rule that allows ICMP traffic¶
Note
If you are not sure about the security group rules, change the protocol and port range to All for testing.
For UDP listeners, see How Does ELB Perform UDP Health Checks? What Are the Precautions for UDP Health Checks?
Checking Firewall Rules¶
Caution
Load balancer: If Cross-VPC Backend is not enabled for a load balancer that has a TCP or UDP listener, there is no need to configure security group rules and firewall rules to allow traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to the backend servers associated with TCP or UDP listener.
To control traffic in and out of a subnet, you can associate a firewall with the subnet. Similar to security groups, firewalls control access to subnets and add an additional layer of defense to your subnets. Default firewall rules reject all inbound and outbound traffic. If the subnet of a load balancer or associated backend servers has a firewall associated, the load balancer cannot receive traffic from the Internet or route traffic to backend servers, and backend servers cannot receive traffic from and respond to the load balancer.
Configure an inbound firewall rule to allow traffic from the VPC where the load balancer works to backend servers.
Log in to the management console.
In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and select the desired region and project.
and select the desired region and project.Hover on
 in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Virtual Private Cloud.
in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Virtual Private Cloud.In the navigation pane on the left, choose Firewall.
In the firewall list, click the name of the firewall to switch to the page showing its details.
On the Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules tab page, click Add Rule to add a rule.
Action: Select Allow.
Protocol: The protocol must be the same as the one you selected for the listener.
Source: Set it to the VPC CIDR block.
Source Port Range: Select a port range.
Destination: If you keep the default value, 0.0.0.0/0, traffic will be allowed for all destination IP addresses.
Destination Port Range: Select a port range.
(Optional) Description: Describe the firewall rule.
Click OK.
Checking the Backend Server¶
Note
If the backend server runs a Windows OS, use a browser to access https://{Backend server IP address}:{Health check port}. If a 2xx or 3xx code is returned, the backend server is running normally.
Run the following command on the backend server to check whether the health check port is listened on:
netstat -anlp | grep port
If the health check port and LISTEN are displayed, the health check port is in the listening state. As shown in Figure 4, TCP port 880 is listened on.
If you do not specify a health check port, backend ports are used by default.

Figure 4 Backend server port listened on¶
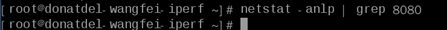
Figure 5 Backend server port not listened on¶
If the health check port is not in the listening state, the backend server is not listened on. You need to start the application on the backend server and check whether the health check port is listened on.
For HTTP health checks, run the following command on the backend server to check the status code:
curl {Private IP address of the backend server}:{Health check port}/{Health check path} -iv
To perform an HTTP health check, the load balancer initiates a GET request to the backend server. If the following response status codes are displayed, the backend server is considered healthy:
TCP listeners: 200
Load balancers: 200 for HTTP/HTTPS health checks
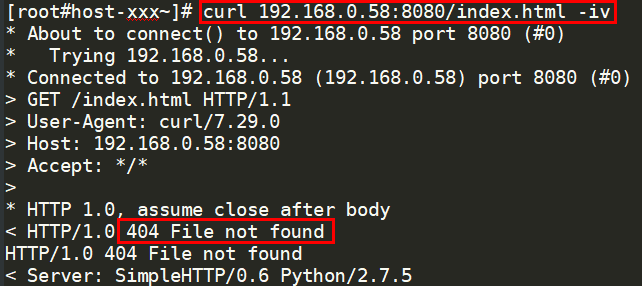
Figure 6 Unhealthy backend server¶
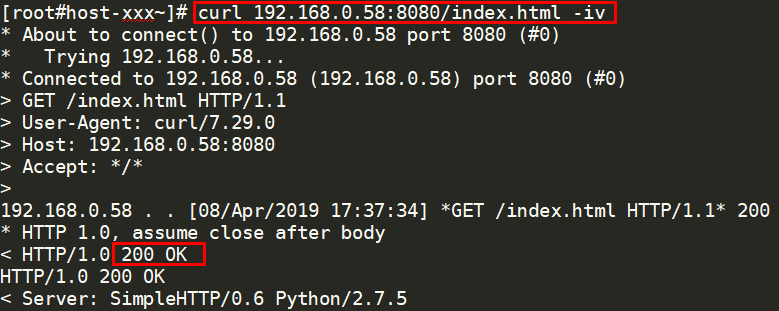
Figure 7 Healthy backend server¶
If HTTP is used for health checks and the backend server is detected unhealthy, perform the following steps to configure a TCP health check:
On the Listeners tab page, modify the listener, select the backend server group for which TCP health check has been configured, or add a backend server group and select TCP as the health check protocol. After you complete the configuration, wait for a while and check the health check result.
Checking the Firewall on the Backend Server¶
If the firewall or other security software is enabled in the backend server, the software may block the IP addresses from the VPC where the load balancers work. Configure inbound firewall rules to allow traffic from the VPC CIDR block to the backend servers.
Checking the Backend Server Route¶
Check whether the default route configured for the primary NIC has been manually modified. If the default route is changed, health check packets may fail to reach the backend server.
Run the following command on the backend server to check whether the default route points to the gateway (For Layer 3 communications, the default route must be configured to point to the gateway of the VPC subnet where the backend server resides):
ip route
Alternatively, run the following command:
route -n
Figure 8 shows the command output when the backend server route is normal.
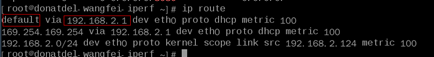
Figure 8 Example default route pointing to the gateway¶
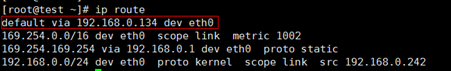
Figure 9 Example default route not pointing to the gateway¶
If the command output does not contain the first route, or the route does not point to the gateway, configure or modify the default route to point to the gateway.
Checking the Backend Server Load¶
View the vCPU usage, memory usage, network connections of the backend server on the Cloud Eye console to check whether the backend server is overloaded.
If the load is high, connections or requests for health checks may time out.
Checking the host.deny File¶
Verify that IP addresses from the VPC where the load balancers work are not written into the /etc/hosts.deny file.