Configuring Hybrid Load Balancing¶
Scenarios¶
You can add servers in the VPC where the load balancer is created, in a different VPC, or in an on-premise data center, by using private IP addresses of the servers. In this way, incoming traffic can be flexibly distributed to cloud servers and on-premises servers for hybrid load balancing.
To add servers in the same VPC as the backend server group, see Adding or Removing Backend Servers.
To add backend servers in a VPC that is not the VPC where the load balancer is running, you need to establish a VPC peering connection between the two VPCs. For details about how to create a VPC peering connection, see the Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
To add on-premises servers to a backend server group, you need to connect the on-premises data center to the VPC where the load balancer is running through Direct Connect or VPN. For details about how to connect on-premises data centers to the cloud, see the Direct Connect User Guide or Virtual Private Network User Guide.
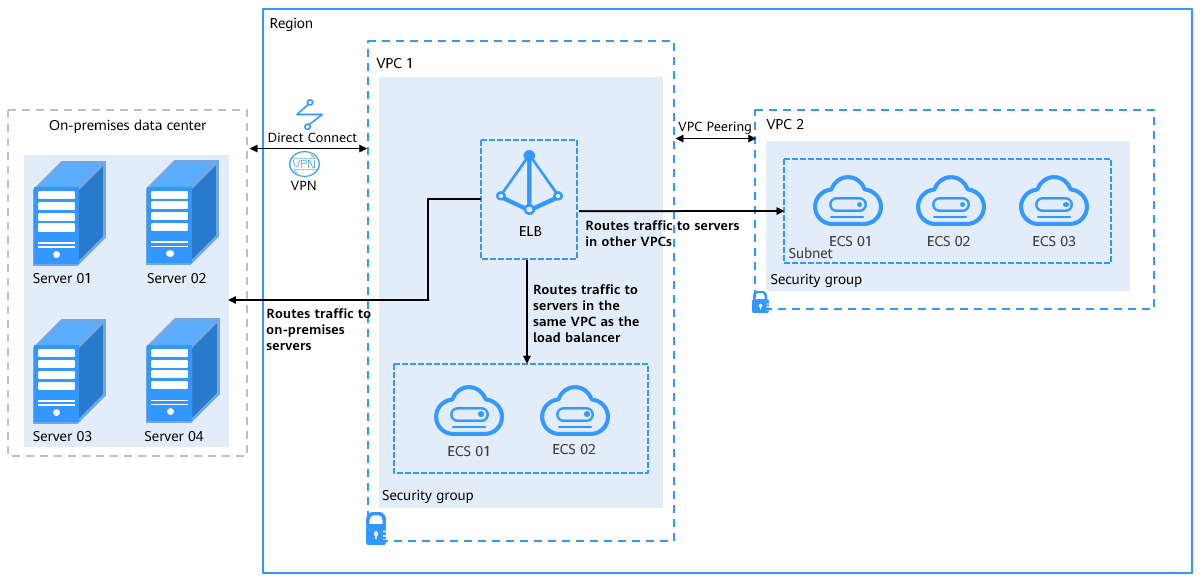
Figure 1 Routing requests to cloud and on-premises servers¶
Prerequisites¶
A load balancer has been created.
A listener has been added to the load balancer.
VPC routes have been correctly configured to make backend servers accessible. Cross-VPC backend servers can be in a VPC connected using a cloud connection or VPC peering connection, or in an on-premises data center connected using a Direct Connect or VPN connection.
Constraints and Limitations¶
When you add cross-VPC backend servers, note the following:
If you do not enable the function when you create a load balancer, you can still enable it on the Basic Information page of the load balancer.
Cross-VPC backend servers must use IPv4 addresses.
If you enable cross-VPC backend for a load balancer, you can add only TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS listeners to the load balancer.
The subnet where the load balancer works must have sufficient IP addresses. Otherwise, cross-VPC backend servers cannot be added. You can add more subnets for more IP addresses on the Basic Information page of the load balancer.
Security group rules of cross-VPC backend servers must allow traffic from the subnet of the load balancer. Otherwise, health checks will fail.
CAUTION: Cross-VPC backend cannot be disabled after it is enabled.
Up to 496 backend servers (including common backend servers and cross-VPC backend servers) can be associated with a listener.
Enabling Cross-VPC Backend¶
Log in to the management console.
In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and select the desired region and project.
and select the desired region and project.Hover on
 in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balancing.
in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balancing.On the Load Balancers page, locate the load balancer and click its name.
On the Basic Information tab page, click Enable next to Cross-VPC Backend.
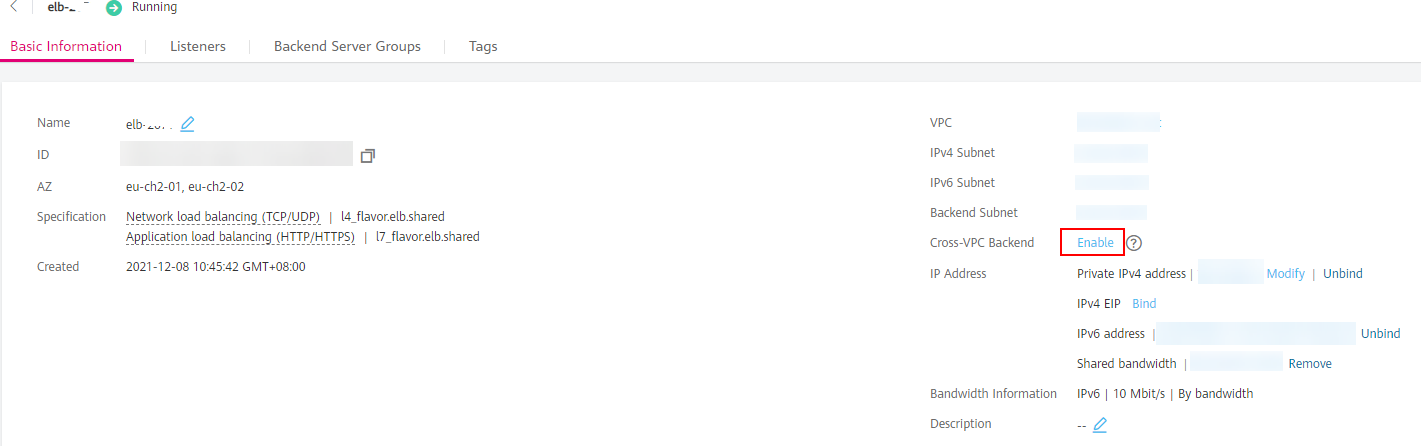
Figure 2 Enabling Cross-VPC Backend¶
Click OK.
Adding Cross-VPC Backend Servers¶
Log in to the management console.
In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and select the desired region and project.
and select the desired region and project.Hover on
 in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balancing.
in the upper left corner to display Service List and choose Network > Elastic Load Balancing.On the Load Balancers page, locate the load balancer that you have created and click its name.
In the Backend Server Groups tab, locate the backend server group and click its name.
In the Basic Information area on the right, click Cross-VPC Backend Servers.
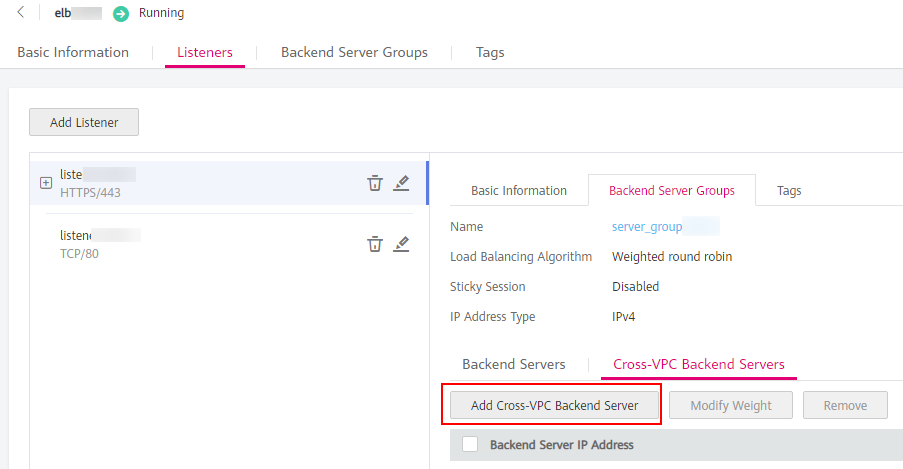
Figure 3 Adding cross-VPC backend servers¶
Click Add Cross-VPC Backend Server and set the IP address, backend port, and weight.
NoteEnsure that the IP addresses of the servers are reachable and the backend ports are actually used by backend servers. Otherwise, the backend servers will be considered unhealthy.
Click OK.