Response¶
Status Code¶
After sending a request, you will receive a response, including a status code, response header, and response body.
A status code is a group of digits, ranging from 1xx to 5xx. It indicates the status of a request. For more information, see HTTP Status Codes.
For example, if status code 201 is returned for calling the API used to obtain a user token, the request is successful.
Response Header¶
Similar to a request, a response also has a header, for example, Content-Type.
Figure 1 shows the response header fields for the API used to obtain a user token. The X-Subject-Token header field is the desired user token. This token can then be used to authenticate the calling of other APIs.
Note
For security purposes, you are advised to set the token in ciphertext in configuration files or environment variables and decrypt it when using it.
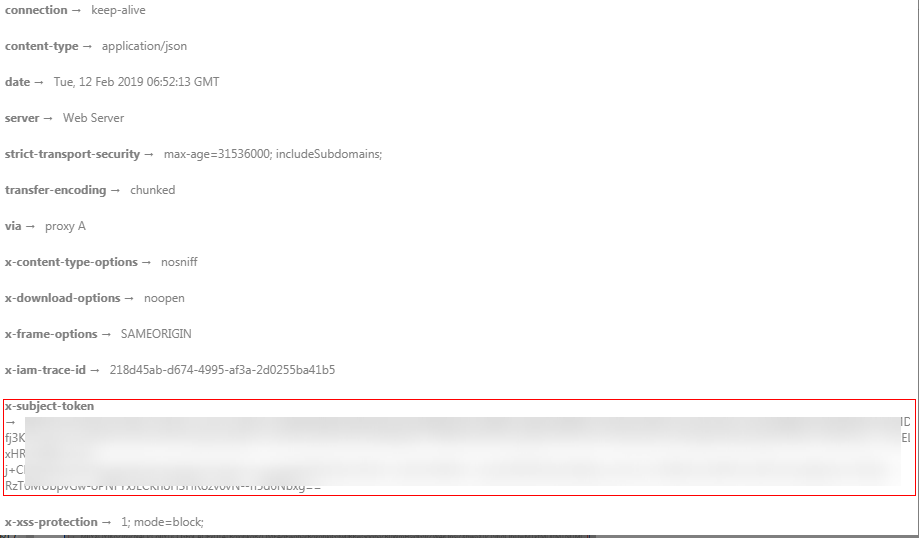
Figure 1 Header fields of the response to the request for obtaining a user token¶
(Optional) Response Body¶
The body of a response is often returned in a structured format (for example, JSON or XML) as specified in the Content-Type header field. The response body transfers content except the response header.
The following is part of the response body for the API used to obtain a user token.
{
"token": {
"expires_at": "2019-02-13T06:52:13.855000Z",
"methods": [
"password"
],
"catalog": [
{
"endpoints": [
{
"region_id": "az-01",
......
If an error occurs during API calling, an error code and a message will be displayed. The following shows an error response body.
{
"error_msg": "The request message format is invalid.",
"error_code": "IMG.0001"
}
In the response body, error_code is an error code, and error_msg provides information about the error.