Creating a Virtual Interface¶
Scenarios¶
Create a virtual interface based on service requirements.
Procedure¶
Log in to the management console.
Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project.In the service list in the upper left corner of the page, choose Network > Direct Connect.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Direct Connect > Virtual Interfaces.
Click Create Virtual Interface.
Configure the parameters.
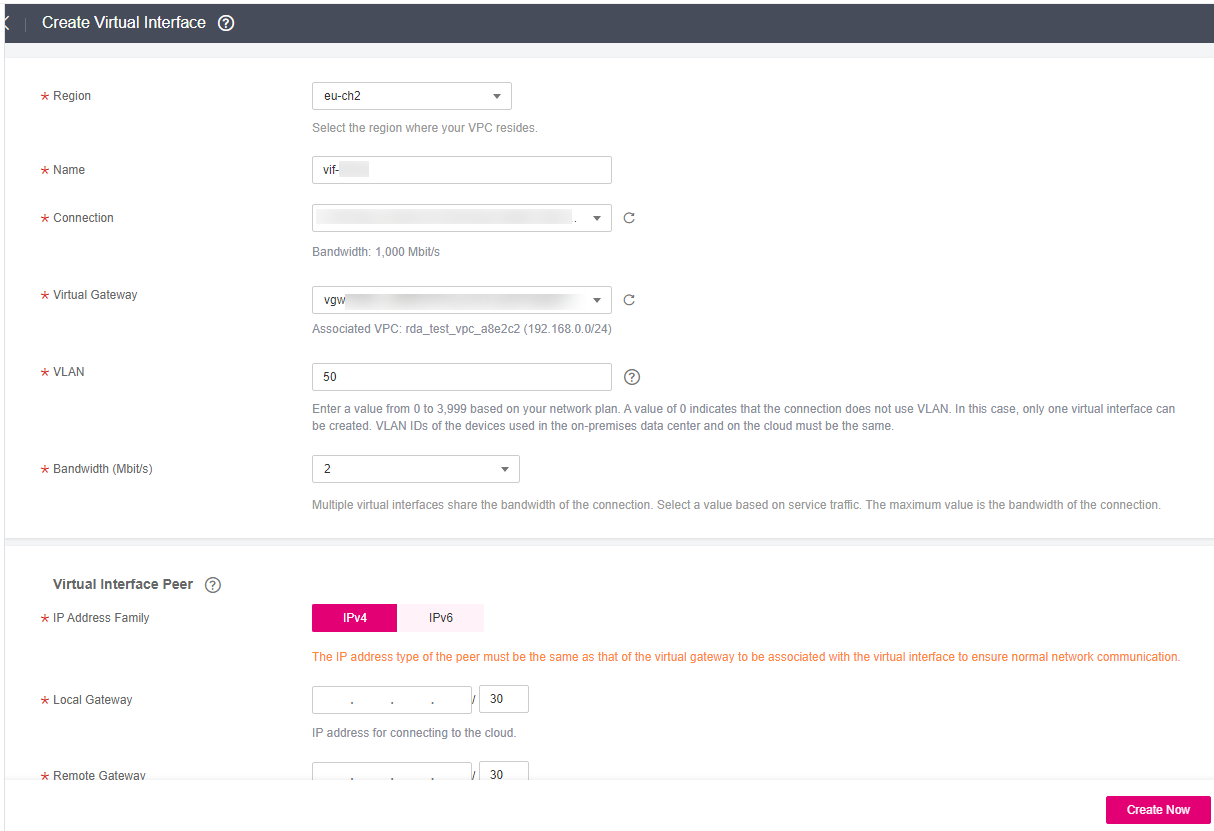
Figure 1 Creating a virtual interface¶
Table 1 Parameters for creating a virtual interface¶ Parameter
Description
Region
Specifies the region where the connection resides. You can change the region in the upper left corner of the console.
Name
Specifies the virtual interface name.
The name can contain 1 to 64 characters.
Only digits, letters, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.) are allowed.
Connection
Specifies the connection you use to connect your on-premises network to the cloud.
Virtual Gateway
Specifies the virtual gateway to which the virtual interface will connect.
VLAN
Specifies the virtual interface VLAN ID.
The value ranges from 0 to 3999.
0 indicates the Layer 3 routing mode. Only one virtual interface can be created for each connection.
You need to configure the VLAN if you create a standard connection.
Bandwidth
Specifies the bandwidth that can be used by the virtual interface, in Mbit/s. The maximum bandwidth of a virtual interface cannot exceed that of the connection.
If Port Type is set to 1GE, the bandwidth ranges from 2 Mbit/s to 1,000 Mbit/s.
If Port Type is set to 10GE, the bandwidth ranges from 2 Mbit/s to 10,000 Mbit/s.
IP Address Family
Specifies the IP version of the virtual interface peer. The value can be IPv4 or IPv6.
Note
The IP address type of the peer must be the same as that of the virtual gateway to be associated with the virtual interface to ensure normal network communication.
Local Gateway
Specifies the IP address for connecting to the cloud network.
Example IPv4 address: 192.168.0.1/30
Example IPv6 address: 1050:326b::/64
Remote Gateway
Specifies the IP address for connecting to your on-premises network.
Example IPv4 address: 192.168.0.2/30
Example IPv6 address: 1060:326b::/64
Remote Subnet
Specifies the subnets of your on-premises network.
Enter one or more unique subnets using CIDR notation and separate each entry with a comma. You can enter up to 50 subnets.
Example IPv4 subnets: 192.168.52.0/24,192.168.54.0/24
Example IPv6 subnets: 1050:326b::/64,1250:5:300c::/64
Caution
CAUTION:
Remote subnets cannot overlap with local subnets.
Using 100.64.0.0/10 as the remote subnet may cause services such as OBS, DNS, and API Gateway to become unavailable.
Routing Mode
Specifies the routing mode. Two options are available, Static and BGP.
If there are two or more connections, select BGP routing.
BGP ASN
Specifies the ASN of the BGP peer.
This parameter is mandatory when you select BGP for Routing Mode.
The value ranges from 1 to 4294967295. Do not use 64512, because it is used by the cloud.
BGP MD5 Authentication Key
Specifies the password used to authenticate the BGP peer using MD5. The value is case sensitive and cannot contain spaces.
This parameter is mandatory when you select BGP routing. You must ensure that the passwords on both gateways are the same.
The password can contain 8 to 255 characters.
The password must contain at least two types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters ~`!,
.:;-_?"(){}[]/@#$%^&*+|\=
Description
Provides supplementary information about the virtual interface.
Note
When you configure the local and remote gateways, note the following:
Local gateway is used by the cloud for connecting to your on-premises network. After you configure Local Gateway on the console, the configuration will be automatically delivered to the gateway used by the cloud.
Remote gateway is used by your on-premises network for connecting to the cloud. After you configure Remote Gateway on the console, you also need to configure the gateway deployed in your equipment room.
The local gateway must be in the same CIDR block as the remote gateway, and this CIDR block cannot conflict with the local subnet configured on the virtual gateway or the remote subnet configured on the virtual interface.
Click Create Now.