What Are Full Backup and Incremental Backup?¶
Description¶
A full backup backs up all data at a certain time point.
An incremental backup backs up the changed data since the last full or incremental backup.
CBR uses the permanent incremental backup technology. A full backup is performed for a resource in the initial backup and incremental backups in subsequent backups. If a full backup expires and is deleted, its next incremental backup will be regarded as the resource's full backup.
Suppose that server X has backups A, B, and C in time sequence. Backup A is a full backup, and backups B and C are incremental backups. Only changed data blocks are backed up in incremental backups and unchanged data blocks are indexed using pointers, so each incremental backup can be regarded as a virtual full backup.
If backup A is deleted, data blocks in backup A indexed by subsequent backups will not be deleted. Only data blocks that are exclusive to backup A are deleted. So, backups B and C can still be used to restore data. Or if backups A and B are deleted, backup C can also be used to restore data independently. There is no obvious difference between their restoration speeds.
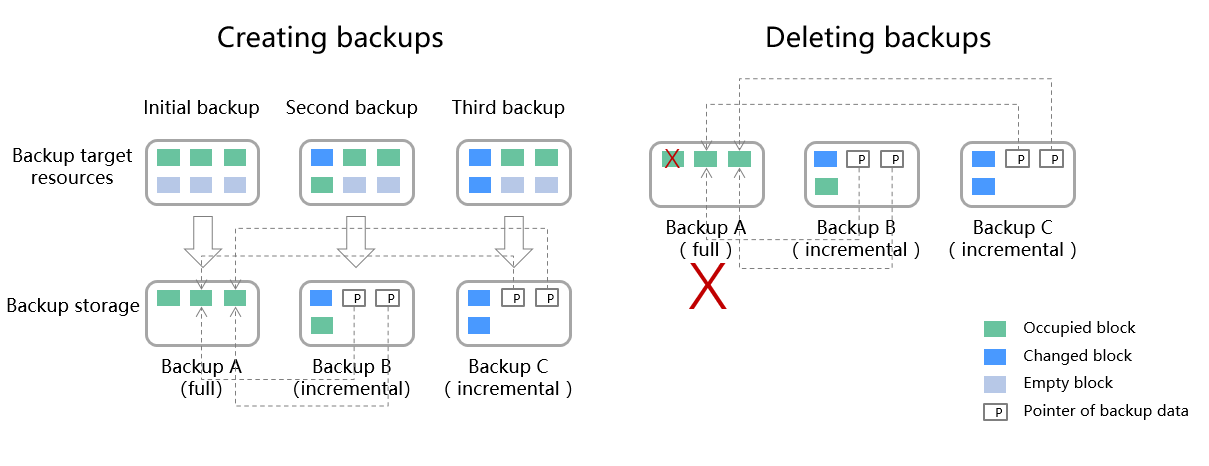
Figure 1 Backup mechanism¶
Differences¶
Backup duration: A full backup backs up the entire resource data which is usually larger than an incremental backup, so full backup take a longer time.
Restoration duration: Both full backups and incremental backups can be restored. There is no obvious difference between their restoration speeds.
Reliability: The latest incremental backup depends on the last full backup and intermediate incremental backups. If any backup data block is damaged, subsequent backups may be affected, which will reduce the backup reliability. All full backup data is independent and does not depend on previous backups. So full backups are more reliable.
You are advised to configure periodic full backup (for example, once every 30 days) and daily incremental backup to reduce the interval of full backup on which incremental backup depends and improve the reliability of backups.
Note
In extreme cases, the size of a backup is the same as the disk size. The used capacity in a full backup and the changed capacity in an incremental backup are calculated based on the data block change in a disk rather than the file change in the operating system. The size of a full backup cannot be evaluated based on the file capacity in the operating system, and the size of an incremental backup cannot be evaluated based on the file size change.