AS Advantages¶
AS automatically scales resources to keep up with service demands based on pre-configured AS policies. With automatic resource scaling, you can enjoy reduced costs, improved availability, and high fault tolerance. AS is used for the following scenarios:
Heavy-traffic forums: The traffic on a popular forum is difficult to predict. AS dynamically adjusts the number of ECS instances based on monitored ECS metrics, such as vCPU and memory usage.
E-commerce: During big promotions, e-commerce websites need more resources. AS automatically increases ECS instances within minutes to ensure that promotions go smoothly.
Live streaming: A livestreaming website may broadcast popular programs from 14:00 to 16:00 every day. AS automatically scales out ECS resources during this period to ensure a smooth viewer experience.
Automatic Resource Scaling¶
AS adds ECS instances for your applications when the access volume increases and removes unneeded resources when the access volume drops, ensuring system stability and availability.
Scaling ECS Instances on Demand
AS scales ECS instances for applications based on demand, improving cost management. ECS instances can be scaled dynamically, on a schedule, or manually:
Dynamic scaling
Dynamic scaling allows scale resources in response to changing demand using alarm-based policies. For details, see Dynamic Scaling.
Scheduled scaling
Scheduled scaling helps you set up your scaling schedule according to predictable load changes by creating periodic or scheduled policies. For details, see Scheduled Scaling.
Manual scaling
You can either manually change the expected number of instances of your AS group, or add or remove instances to or from the AS group. For details, see Manual Scaling.
Consider a train ticket booking application running on the cloud. The load of the application may be relatively low during Q2 and Q3 because there are not many travelers, but relatively high during Q1 and Q4. Traditionally, there are two ways to plan for these changes in load. The first option is to provide enough servers so that the application always has enough capacity to meet demand, as shown in Figure 1. The second option is to provision servers according to the average load of the application, as shown in Figure 2. However, these two options may waste resources or be unable to meet demand during peak seasons. By enabling AS for this application, you have a third option available. AS helps you scale servers to keep up with changes in demand. This allows the application to maintain steady, predictable performance without wasting money on any unnecessary resources, as shown in Figure 3.
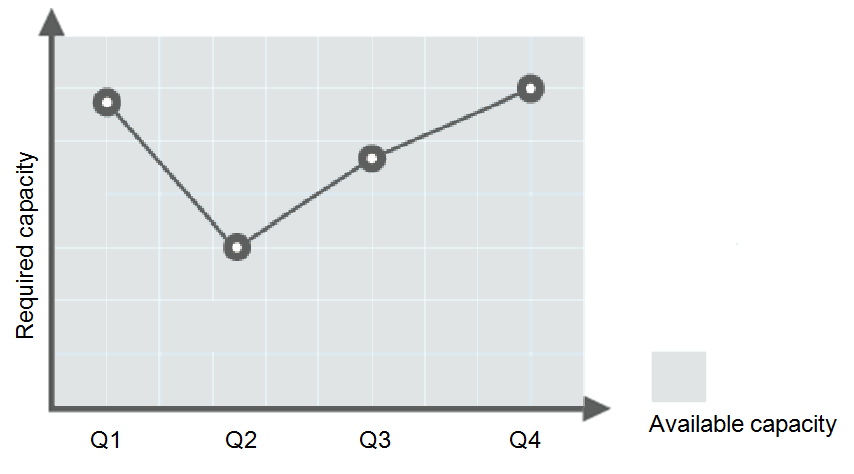
Figure 1 Over-provisioned capacity¶
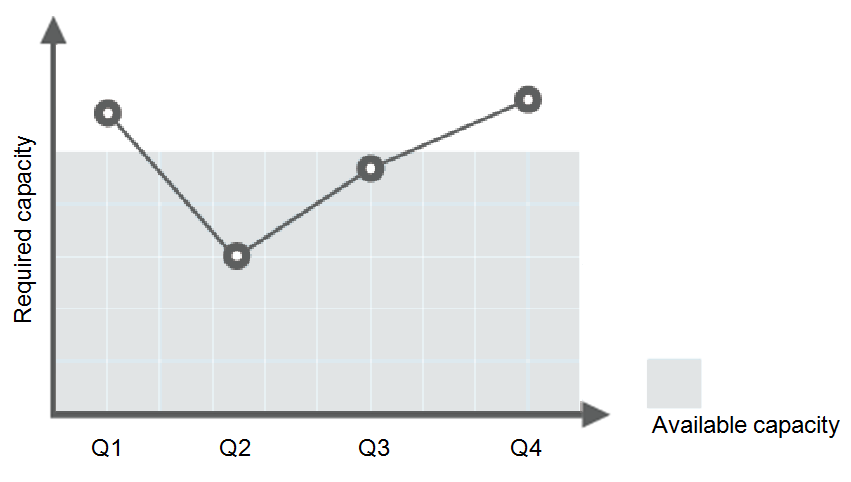
Figure 2 Insufficient capacity¶
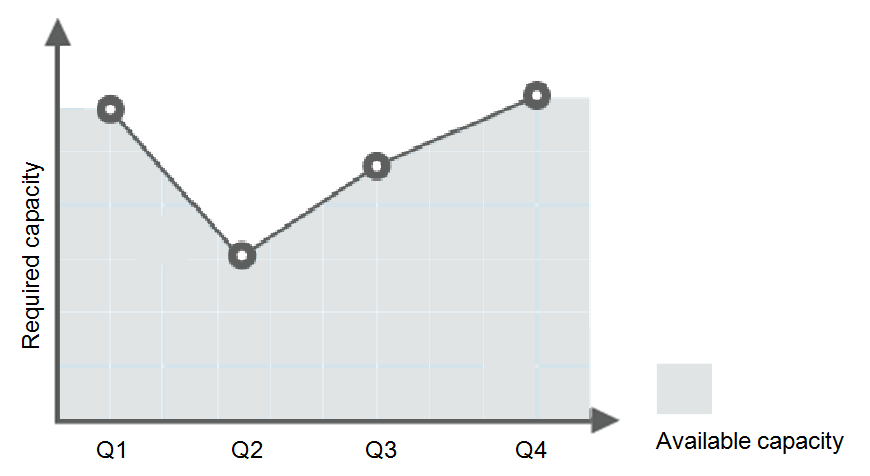
Figure 3 Auto-scaled capacity¶
Scaling Bandwidth on Demand
AS adjusts bandwidth for an application based on demand, reducing bandwidth costs.
There are three types of scaling policies you can use to adjust the IP bandwidth on demand:
Alarm-based policies
You can configure triggers based on metrics such as outbound traffic and bandwidth. When the system detects that the triggering conditions are met, the system automatically adjusts the bandwidth.
Scheduled policies
The system automatically increases, decreases, or adjusts the bandwidth to a fixed value on a fixed schedule.
Periodic policies
The system periodically adjusts the bandwidth based on a configured periodic cycle.
For example, you can use an alarm-based policy to regulate the bandwidth for a livestreaming website.
For a livestreaming website, service load is difficult to predict. In this example, the bandwidth needs to be dynamically adjusted between 10 Mbit/s and 30 Mbit/s based on metrics such as outbound traffic and inbound traffic. AS can automatically adjust the bandwidth to meet requirements. You just need to select the relevant EIP and create two alarm policies. One policy is to increase the bandwidth by 2 Mbit/s when the outbound traffic is greater than X bytes, with the limit set to 30 Mbit/s. The other policy is to decrease the bandwidth by 2 Mbit/s when the outbound traffic is less than X bytes, with the limit set to 10 Mbit/s.
Evenly Distributing Instances by AZ
To reduce the impact of power or network outage on system stability, AS attempts to distribute ECS instances evenly across the AZs that are used by an AS group.
A region is a geographic area where resources used by ECS instances are located. Each region contains multiple AZs where resources use independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated from one another but interconnected through an intranet. AZs are engineered to be isolated from failures in other AZs. They provide cost-effective, low-latency network connections to other AZs in the same region.
An AS group can contain ECS instances in one or more AZs within a region. When scaling the capacity of an AS group, AS attempts to evenly distribute ECS instances across AZs used by the AS group based on the following rules:
Evenly distributing new instances to balanced AZs
AS attempts to evenly distribute ECS instances across the AZs used by an AS group. To do it, AS adds new instances to the AZ with the fewest instances.
Consider an AS group containing four instances that are evenly distributed in the two AZs used by the AS group. If a scaling action is triggered to add four more instances to the AS group, AS adds two to each AZ.
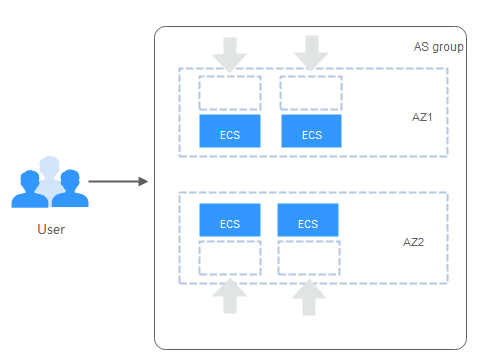
Figure 4 Evenly distributing instances¶
Re-balancing instances across AZs
After you have manually added or removed instances to or from an AS group, the AS group can become unbalanced between AZs. AS compensates by re-balancing the AZs during the next scaling action.
Consider an AS group containing three instances that are distributed in AZ 1 and AZ 2, with two in AZ 1 and one in AZ 2. If a scaling action is triggered to add five more instances to the AS group, AS adds two to AZ 1 and three to AZ 2.
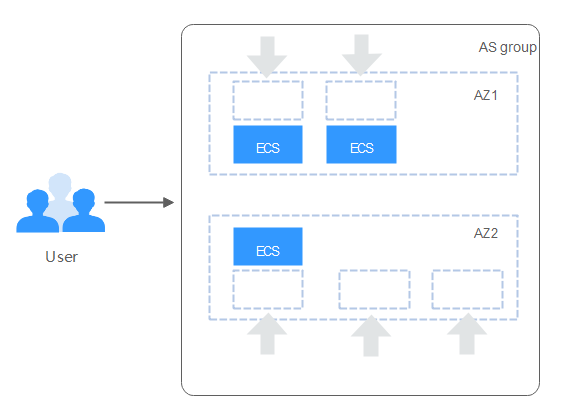
Figure 5 Re-balancing instances¶
Enhanced Cost Management¶
AS enables you to use ECS instances on demand by automatically scaling resources for your applications, eliminating waste of resources and reducing costs.
Higher Availability¶
AS ensures that you always have the right amount of resources available to handle the fluctuating load of your applications.
Using ELB with AS
Working with ELB, AS automatically scales ECS instances based on changes in demand while ensuring that the load of all the instances in an AS group stays balanced.
After ELB is enabled for an AS group, AS automatically associates a load balancing listener with any instances added to the AS group. Then, ELB automatically distributes traffic to all healthy instances in the AS group through the listener, which improves system availability. If the instances in the AS group are running a range of different types of applications, you can bind multiple load balancing listeners to the AS group to listen to each of these applications, improving service scalability.
High Fault Tolerance¶
AS monitors instances in an AS group, and replaces any unhealthy instances it detects with new ones.