Dashboard¶
With a dashboard, different graphs can be displayed on the same screen. Different graphs, such as line graphs and digit graphs can be used to display resource data, so that you can view monitoring data comprehensively.
You can add key resource metrics to a dashboard and monitor them in real time. You can also compare the same metric of different resources on one screen. In addition, by adding routine O&M metrics to a dashboard, you can perform routine checks without re-selecting metrics when you open AOM again.
Before creating a dashboard, learn the types of graphs that can be added to a dashboard for accurate resource monitoring. The following graphs can be added to a dashboard:
Metric Data Graphs (Including Line and Digit Graphs)¶
Line graph: displays the metric data trend by time. Use this type of graph to monitor the metric data trend of one or more resources in a period. Titles of metric data graphs can be customized.
You can use a line graph to compare the same metric of different resources. The following figure shows the CPU usage of different hosts.
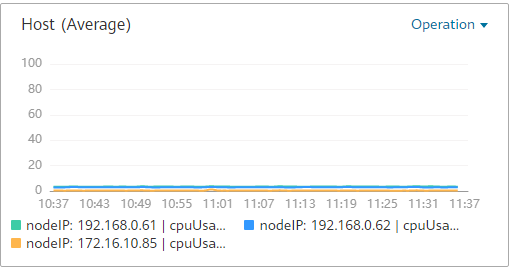
Figure 1 Line graph¶
Digit graph: displays the latest value of a metric in real time.
The following figure shows the latest CPU usage.
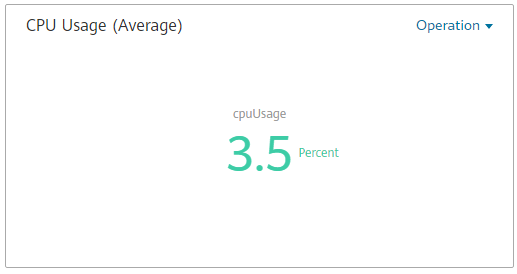
Figure 2 Digit graph¶
Health Status Graphs (Including Threshold, Host, and Component Status Graphs)¶
The statuses of thresholds, hosts, and components can be displayed. The statuses of one or more threshold rules, hosts, or components can be added in one graph for monitoring. Titles of health status graphs can be customized.
Threshold-crossing status graph: monitors the status of alarm rules in real time.
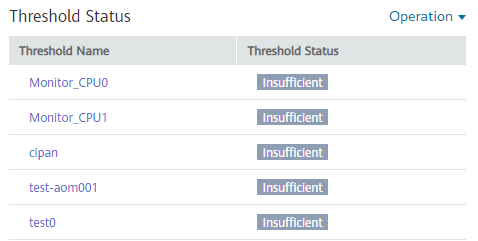
Figure 3 Threshold-crossing status graph¶
Note
Before adding a threshold-crossing status graph, create an alarm rule. Otherwise, the threshold-crossing status graph cannot be added.
Host status graph: monitors the health status of hosts in real time.
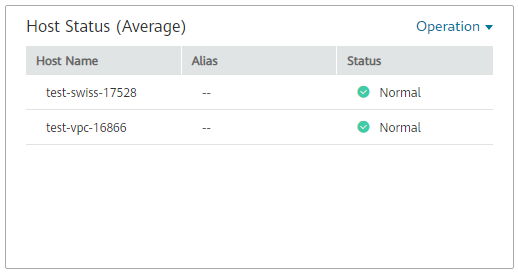
Figure 4 Host status graph¶
Component status graph: monitors the health status of components in real time.
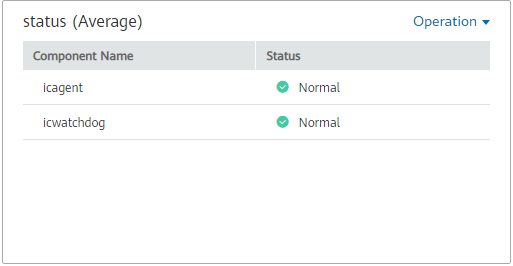
Figure 5 Component status graph¶
Top N Resource Graphs¶
For top N resource graphs, the statistical unit is a cluster and statistical objects are resources such as hosts, components, or instances in the cluster. A top N resource graph shows the top N resources in a cluster in a visualized manner. Both the top 5 and top 15 resources can be displayed. By default, the top 5 resources are displayed. After the graph is zoomed in, the top 15 resources are displayed.
To quickly view the top N resources, add a top N graph to the dashboard. You only need to select resources and metrics, for example, host CPU usage. AOM then automatically singles out the top N hosts for display. If the number of resources is less than N, actual resources are displayed. The following figure lists the top 5 instances with the highest CPU usage.
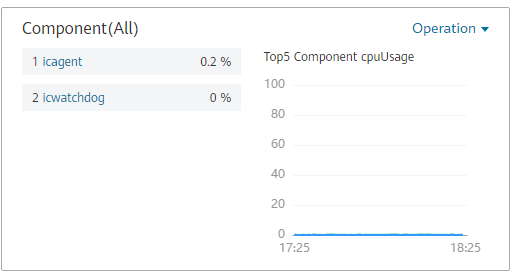
Figure 6 Top N resource graph¶
Note
By default, the top 5 resources are displayed. To view the top 15 resources, click Show Top15, double-click the graph, or click View Larger in the Operation column.
To monitor the top 5 resources among all clusters, view them on the O&M page.
You can customize the title of the top N resource graph. By default, the title is resource type(cluster name).
Precautions¶
A maximum of 50 dashboards can be created in a region.
A maximum of 20 graphs can be added to a dashboard.
A maximum of 100 resources can be added to a line graph, and resources can be selected across clusters.
Only one resource can be added to a digit graph.
A maximum of ten threshold rules can be added to a threshold-crossing status graph.
A maximum of ten hosts can be added to a host status graph.
A maximum of ten components can be added to a component status graph.
Creating a Dashboard¶
In the navigation pane, choose Overview > Dashboard.
On the Dashboard page, click Create Dashboard. In the displayed dialog box, enter a dashboard name and click OK.
Click Add Metric Graph in the upper right corner of the Dashboard page. Then, select Metric Data, Health Status, or Top N Resources.
Add a metric graph to the dashboard.
Under Metric Data, line and digit graphs can be selected.
Under Health Status, threshold-crossing status graphs, host status graphs, and component status graphs can be selected.
Select a graph that is appropriate for your requirements. The following shows how to add a line graph to a dashboard:
On the Dashboard page, click Add Metric Graph. In the displayed Select Which to Add dialog box, click Create below Metric Data.
Select the type of the graph: In the displayed Add Metric Graph dialog box, select Line graph and then click Next.
Set a metric graph: Set a graph title, select a resource type, select the resource to be monitored from the resource tree on the left, select a metric, set a statistical method and period, and click OK.
Click Save in the upper right corner of the Dashboard page.
Note
The Auto Refresh (
 ) option in the upper right corner of the Dashboard page can be enabled to automatically refresh all graphs in the dashboard.
) option in the upper right corner of the Dashboard page can be enabled to automatically refresh all graphs in the dashboard.On (default)
Data in the dashboard is automatically refreshed every minute.
Off
Data in the dashboard is not automatically refreshed.
More Operations¶
After creating a dashboard, you can also perform the operations described in Table 1.
Operation Object | Operation | Description |
|---|---|---|
Dashboard | Save as | Click More in the upper right corner, and choose Save As, Rename, or Delete from the drop-down list. |
Rename | ||
Delete | ||
Set an interpolation mode | For details, see Table 2. | |
Export a monitoring report | Click Export Monitoring Report to export line graphs in the dashboard as CSV files to a local PC. | |
Set the query time | In the upper right corner of the Dashboard page, set a time range and statistical cycle to query the dashboard data.
| |
Graph | Add | Click Add Metric Graph to add a line graph, digit graph, threshold-crossing status graph, host status graph, component status graph, or top N resource graph to the dashboard. |
Edit | Choose Edit, Copy, Delete, or View Larger (support only for line graphs) from the Operation drop-down list. The Time Select option is available only in a line graph. This option allows you to set a temporary time range and statistical cycle so that you can view the resource data within a specified time range. Note In the dashboard, when resources such as hosts and components are deleted, graphs created for these resources are not automatically deleted. To improve system performance, manually delete unnecessary graphs. | |
Copy | ||
Delete | ||
Zoom in | ||
Time select | ||
Refresh | ||
Resize | Hover over the lower right corner of a graph. When the cursor changes to | |
Reposition | Hover over the blank area in the upper or lower part of a graph, and drag and drop it to the desired position. |
 , hold down your left mouse button to resize the graph.
, hold down your left mouse button to resize the graph.