Creating Alarm Rules¶
You can set threshold conditions for metrics by using alarm rules. If metric values meet threshold conditions, AOM will generate threshold alarms. If no metric data is reported, AOM will report insufficient data events. In this way, you can identify and handle exceptions at the earliest time.
For example, during routine O&M, a host may break down or restart due to an excessively-high CPU usage. To avoid the problem, set an alarm rule. For example, when the CPU usage of a host exceeds 85%, an alarm is reported, so that you can quickly obtain the resource running status and take measures to prevent service loss.
Precautions¶
You can create a maximum of 1000 alarm rules. If the number of alarm rules reaches the upper limit, delete unnecessary rules and create new ones.
Customizing Alarm Rules¶
In the navigation pane, choose Alarm Center > Alarm Rule and click Add Threshold.
Customize alarm rules.
Select resources: Enter a threshold rule name, select a resource type, select the resources to be monitored from the resource tree, and click Next.
Note
You can select a maximum of 100 resources from the resource tree.
When multiple resources are selected, multiple alarm rules will be created after the creation is complete. Each resource is monitored by an alarm rule. A rule name consists of the alarm rule name you enter in the Threshold Name text box, and a sequence number ranging from 0 to 99. The earlier a resource is selected, the smaller its sequence number.
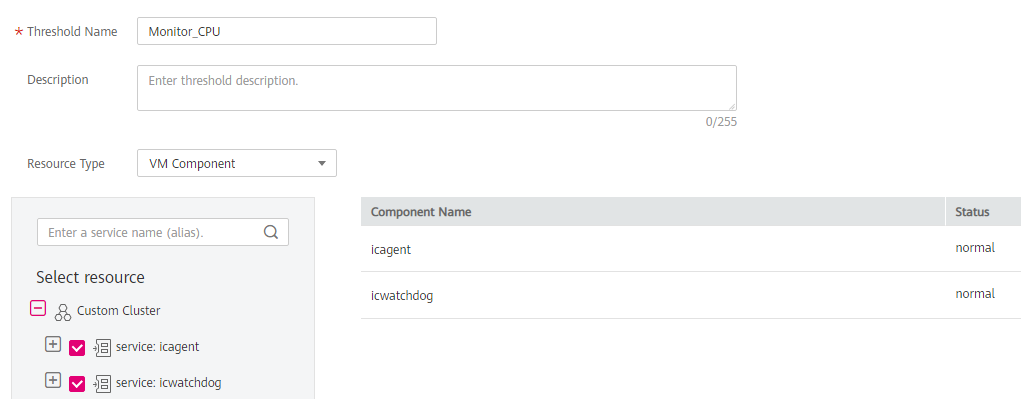
Figure 1 Selecting resources¶
Customize a threshold: Select the metric to be monitored, and set parameters such as Threshold Condition, Consecutive Period (s), Alarm Severity, and Statistic Method.
Note
Threshold Condition: Trigger condition of a threshold alarm. A threshold condition consists of two parts: determination condition (>=, <=, >, or <) and threshold value. For example, if Threshold Condition is set to > 85 and an actual metric value exceeds 85, a threshold alarm will be generated.
Consecutive Period (s): If a metric value meets the threshold condition for a specified number of consecutive periods, a threshold alarm will be generated.
Alarm Severity: Critical, Major, Minor, or Warning.
Statistic Method: Method used to measure metric values.
Statistical Cycle: Interval at which metric data is collected.
Click Submit. As shown in the following figure, multiple alarm rules are created. Each resource is monitored by an independent rule.
For example, when a monitored component uses more than 3 CPU cores, a threshold alarm is generated on the alarm page. You can choose Alarm Center > Alarm Rule in the navigation pane to view the alarm rule.

Figure 2 Alarm rules¶
More Operations¶
After creating an alarm rule, you can also perform the operations described in Table 1.
Operation | Description |
|---|---|
Modifying an alarm rule | Click Modify in the Operation column. |
Deleting an alarm rule |
|
Searching for an alarm rule | Enter the rule name or description in the search box in the upper right corner and click |
Viewing an alarm rule | Click |
Viewing an alarm | If the metric value of a resource meets a threshold condition in the specified number of consecutive periods, a threshold alarm will be sent. In the navigation pane, choose Alarm Center > Alarm List to view the alarm. |
Viewing an event | During the configured consecutive periods, if no metric data of a resource is reported, an insufficient data event will be sent. In the navigation pane, choose Alarm Center > Event List to view the event. |
 to search.
to search. next to an alarm rule to view its details.
next to an alarm rule to view its details.